Advanced Techniques for Vegetation Monitoring With Planetary Variables
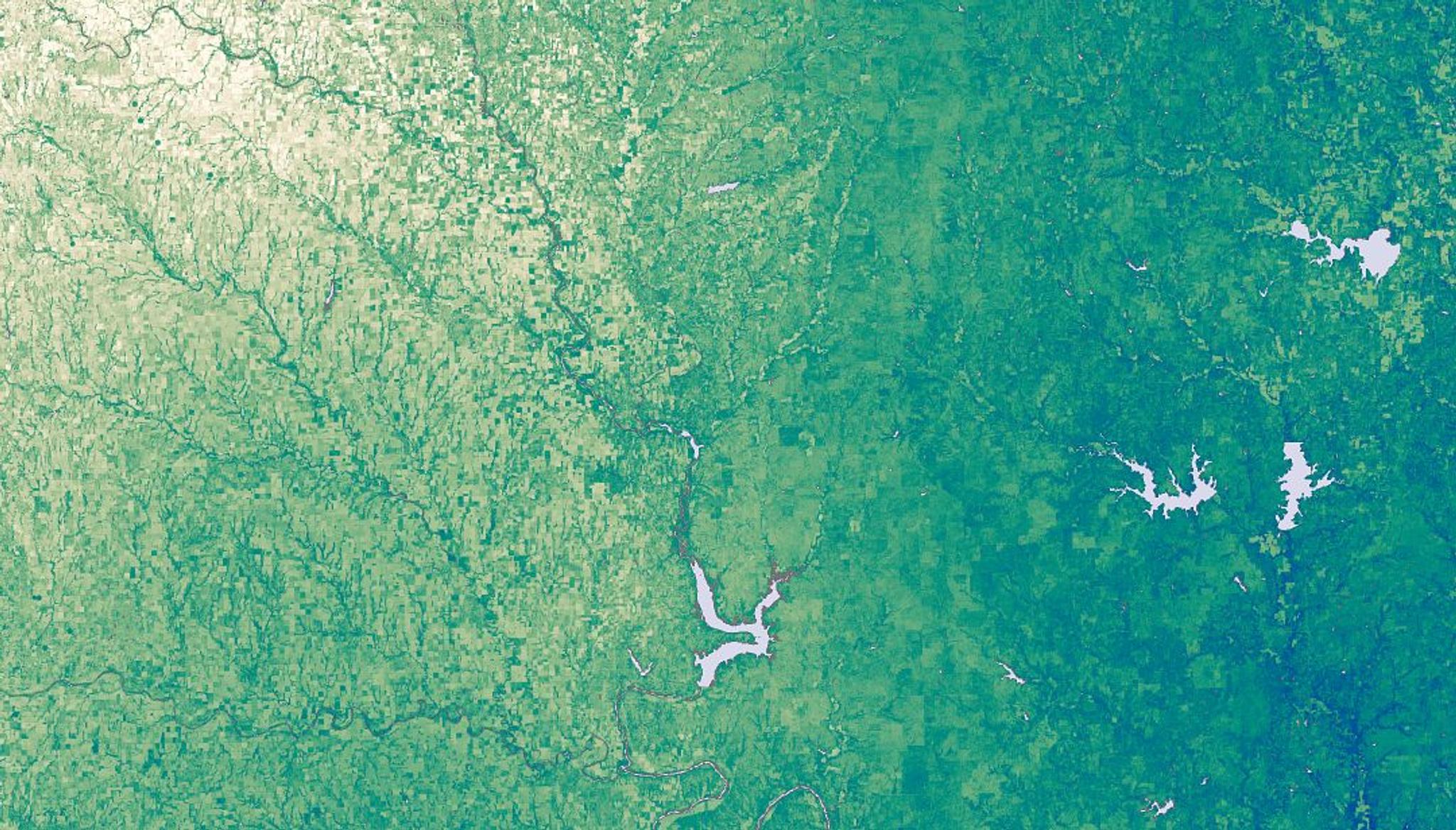

Soil Water Content measurements in Tanzania, June 30 2022. © 2022 Planet Labs PBC. All Rights Reserved.
TechLearn how Planetary Variables can be used to support resource management, environmental assessment, disaster prevention, and more.
Vegetation monitoring involves inspecting and measuring the growth of trees and other plants to understand ecosystem health. Governments and industries need accurate, up-to-date data to assess vegetation health and manage resources effectively.
However, traditional data-gathering methods often fall short. Infrequent surveys, coverage limitations, and slow processing times make it hard for organizations to keep up with vegetation dynamics.
Scientists, GIS analysts, and government agencies increasingly rely on satellite imagery to get a complete picture of conditions on the ground. And as Earth observation (EO) technology advances to include the analysis of multi-spectral bands, this picture can include elements that can not be seen with the naked eye.
Planetary Variables® datasets from Planet provide a whole new way to understand what’s happening on the ground. These products translate raw satellite observations into quantifiable metrics about biophysical properties such as soil moisture, land temperature, crop biomass, and forest carbon stocks.
In this article, we’ll examine the role of Planetary Variables in vegetation monitoring and explore their real-world applications.
The Role of Planetary Variables in Vegetation Monitoring
Many environmental changes influence plant growth and ecosystem health. EO capabilities capture detailed data about a broad range of factors. Planetary Variables products unlock information about the physical properties of Earth by fusing data from a range of sources, including optical, radar, passive microwave, and LiDAR sensors.
Planetary Variables deliver continuous, scientifically rigorous data that measure changing conditions on the Earth’s surface. These unique datasets from across the electromagnetic spectrum offer actionable insights into plant development, land use, and ecological changes.
The suite of Planetary Variables products includes:
- Soil Water Content
- Land Surface Temperature
- Crop Biomass
- Field Boundaries
- Forest Carbon
Let’s take a closer look at each of these data feeds and how they enhance satellite vegetation monitoring programs.
Soil Water Content
The Earth’s water systems are indispensable resources for ecosystems in every corner of the world. They are also complex and dynamic, making them difficult to monitor without accurate and current data.
Soil Water Content is a feed of high-resolution, globally available measurements of the volume of freshwater stored in the soil. Organizations use this data to better understand vegetation health as it relates to agriculture, drought tracking, and other climate risks.
Land Surface Temperature
Rising temperatures across the globe are driving changes in climate patterns that significantly impact the environment and communities.
Land Surface Temperature can help agencies track and respond to these pressures. This Planetary Variable measures the Earth’s skin temperature — providing vital intelligence about our atmosphere, food and water systems, urban living conditions,drought conditions, and vegetation stress.
Crop Biomass
Crop biomass continually changes throughout the growing season as plants encounter stressors and approach harvest. Timely and frequent access to biomass data is essential for understanding these trends and making informed decisions regarding crop and vegetation management.
The Crop Biomass dataset offers daily, cloud-free data that delivers estimates of crop biomass across all weather conditions. It provides valuable insights into crop health to optimize crop health and maximize yields across the agriculture industry.
Field Boundaries
Field boundaries provide a foundational framework for a wide range of analyses related to vegetation management, from sustainable agriculture and supply chain monitoring to estimates of regional food production to assess food security.
The Field Boundaries dataset contains polygons representing the boundaries of agricultural fields in any area of interest around the globe. This dataset is generated by automatically tracing the boundaries of agricultural parcels from satellite imagery for a specified area and time of interest, where each field contains a single crop type.
Forest Carbon
Carbon stored in trees is vital for regulating atmospheric CO2 levels and mitigating climate change.
The Forest Carbon dataset offers up-to-date, accurate, and finely resolved measurements of the aboveground carbon stored in forests, as well as measurements of forest canopy cover and canopy height. These metrics help organizations quantify carbon stocks and deforestation — and monitor general forest and vegetation health.
Application of Planetary Variables for Vegetation Monitoring
Planetary Variables offer concrete data points to support vegetation monitoring, bridging the gap between satellite observations and practical applications. Here are several key use cases:
- Resource management: Planet data delivers insights for efficiently managing natural resources, from forests to water.
- Land-use planning: Vegetation health data can inform wise urban development and agricultural planning.
- Environmental assessment: Closely tracking environmental changes and potential risks aids conservation efforts.
- Disaster prevention: Vegetation changes can signal risk of drought, fire, flood, or landslide in their early stages, allowing for interventions.
- Policy development: Advanced vegetation monitoring informs sustainable land management and resource use policies.
Case Studies Using Planetary Variables for Vegetation Analysis
Given that Earth’s systems are in constant flux, it’s essential for any vegetation monitoring program to have fresh and highly-detailed data. Planet’s broad-spectrum satellite data provides a more comprehensive and up-to-date view of changing environmental conditions and plant growth than conventional vegetation biomass analysis could alone.
Many civil government agencies, non-government organizations, and businesses use Planetary Variables to monitor droughts and wildfires, assess fire and flood risk, track growing seasons, and more.
Protecting Farmers With Sophisticated Drought Index Insurance
French climate consulting company AXA Climate uses Soil Water Content monitoring to offer highly responsive drought insurance policies. AXA’s parametric insurance product estimates crop yields and losses based on Soil Water Content data and can compensate farmers, processors, and other stakeholders within days of the end of a risk period.
“With Planet’s unique satellite data, AXA Climate has been able to provide a high-quality index insurance coverage service for farmers and cooperatives,” said Antoine Denoix, CEO of AXA Climate. “We can now act quickly to help farmers and stakeholders combat the major threat of drought to agriculture around the world.”
Proving NGO Impact Using Surface Temperature and Soil Moisture
In the Horn of Africa, NGO Justdiggit uses nature-based solutions to regreen warming and drying landscapes. They leverage Planet Land Surface Temperature and Soil Water Content data to quantify the impact of their landscape restoration work.
By measuring the soil moisture over time where the regreening took place, as well as nearby sites with no intervention, they capture the long term impact of their efforts. Land Surface Temperature data shows a similar shift in the conditions of the soil. The temperature of the restored sites is consistently lower over time, than the control sites.
As Sander de Haas, Chief Technical Officer at Justdiggit, explains, “We want to reach and activate 350 million farmers across Africa with our platform, so a drone won’t cover it. We need the satellites to really show the impact on the entire African continent.”
Optimizing Crop Monitoring to Maximize Agricultural Yield
Using traditional techniques, clouds and other adverse weather conditions can potentially impact the capture of biomass data. Planet overcomes this challenge by combining optical imagery and microwave technology to provide accurate, high-resolution Crop Biomass data in any weather.
Disagro, an international corporation based in Guatemala, is a leader in agricultural innovation and a Planet customer. “Crop Biomass is a highly valuable and complementary service for us and our clients whose areas of focus are often affected by high cloud cover. Strategic partners like Planet provide us with the technical support needed to increase the usability of satellite imagery and bring Digital Agriculture practices to our regions under management.”
Harnessing the Power of Planetary Variables
GIS analysts, government officials, scientists, and other professionals stand to benefit tremendously from using advanced satellite imagery to build or enhance vegetation monitoring programs.
Better data leads to more informed decision-making and more scientifically rigorous sustainable practices. Our Planetary Variables — Crop Biomass, Forest Carbon, Land Surface Temperature, and Soil Water Content — can enable detailed maps, comprehensive land use monitoring, earlier detection of signs of environmental stress, and more efficient resource management.
Ready to unlock the full potential of advanced techniques in vegetation monitoring? Explore Planetary Variables, an advanced suite of monitoring solutions designed to take your efforts to the next level.
Connect with our sales team today to learn more!

Ready to Get Started
Connect with a member of our Sales team. We'll help you find the right products and pricing for your needs.