Monitoring Coastal Habitats That Support Local Communities and Diverse Ecosystems
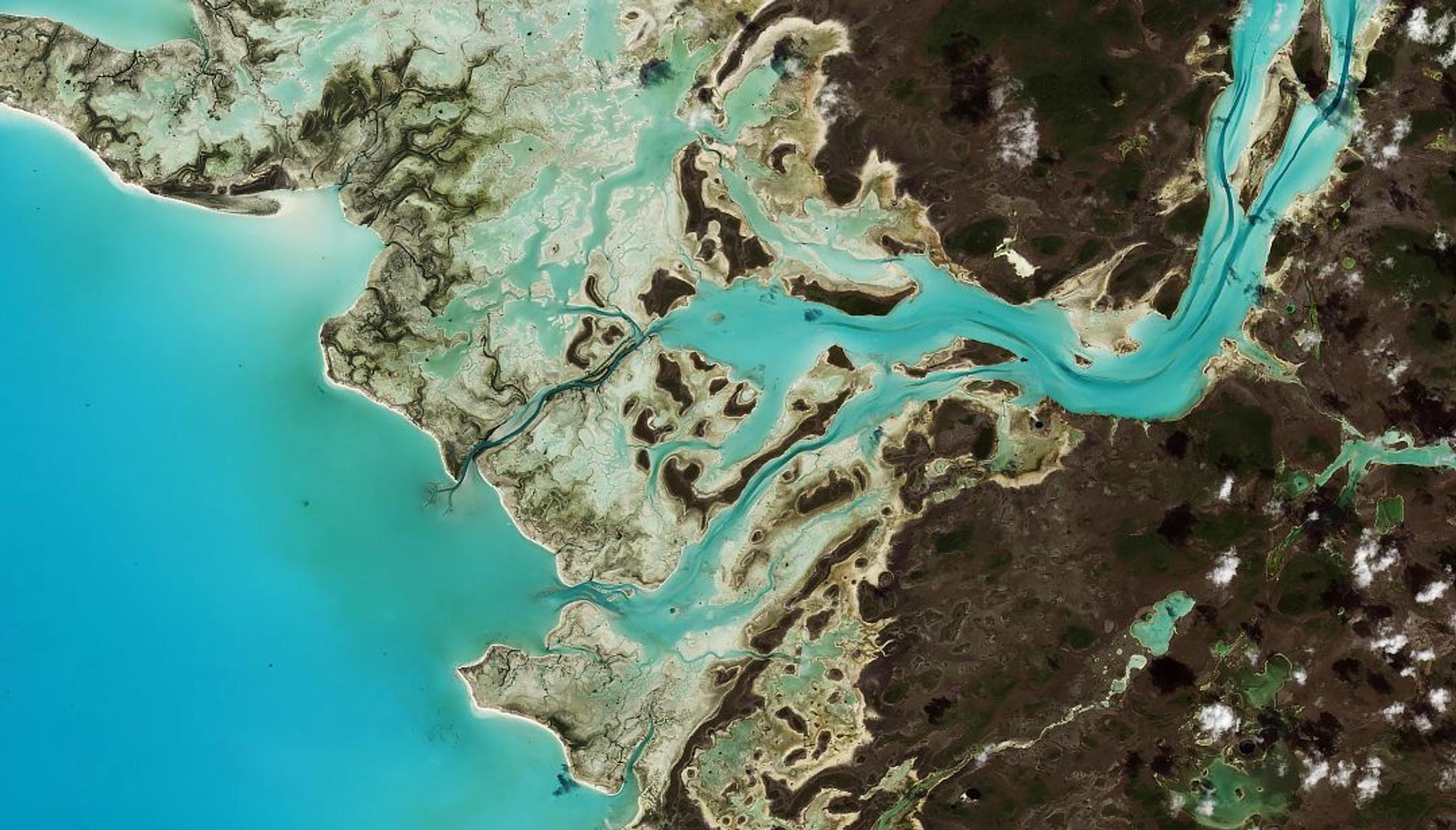

PlanetScope image of coastal vegetation in Tarpon Town, Andros Island, The Bahamas, captured February 10, 2023. © 2023 Planet Labs PBC. All Rights Reserved.
TechLearn how high-frequency satellite imagery can minimize the threats that coastal habitats face from climate change and human activities.
Coastal habitats, including marshes and wetlands, serve as lifelines for surrounding human communities and marine ecosystems. Maintaining the health of coastal zones is vital to sustaining biodiversity, ensuring food security, and promoting resilience against climate change.
High-frequency Earth data and analytics from Planet help agencies regularly monitor conditions in coastal environments, at any scale. This practice – known as broad area management – allows authorities to maximize efficiency and catch unexpected events early, reducing risk to ecosystems and communities.
Let’s explore how broad area management with Planet can help policymakers and agencies better monitor and protect these complex and vital habitats.
Change Is a Constant in Coastal Habitats
Wetlands, mangroves, seagrass meadows, coral reefs, and other coastal ecosystems have enormous value. Not only are they home to a rich and diverse range of plants and animals, but they are closely intertwined with surrounding cities and towns. By supporting tourism, fishing, and other industries they are catalysts for overall economic growth. In addition, they serve as buffers against storm surges and extreme weather.
However, these valuable habitats are some of the most dynamic and vulnerable landscapes on Earth. Water levels are in constant motion because of tides and storms; and human activities like urban development, tourism, and nearshore dredging bring additional change.
All of these conditions make coastal ecosystems difficult to monitor. In addition, many governments conduct coastal surveys only every two to six years. This low-frequency data makes it hard to set an accurate baseline for trends over time and or understand how an area responds to specific disturbances or projects.
As climate change and human activity put an ever-greater strain on these habitats, officials are seeking new coastal habitat monitoring strategies to help protect these environments and the communities they support.
Leveraging Broad Area Management With Planet for Coastal Monitoring
Broad area management is the practice of leveraging Earth observation data to monitor, measure, and report changes across vast geographic areas.
Planet’s approach to broad area management brings together daily monitoring, hi-resolution imagery, analysis-ready data, and analytics to help governments identify relevant change, validate hazards, and respond swiftly.
PlanetScope®Monitoring provides a near-daily scan of the Earth, including a comprehensive view of coastal zones spanning vast areas and regions inaccessible to humans.
High-resolution Planet Tasking provides a more detailed view of any area of interest to help quantify the impact of storms, flooding, or other events.
And when this data is combined with Planet Archive, which includes proprietary datasets back to 2009 and public datasets back to 1972, analysts can establish a baseline and measure changes on multiple time scales.
Together, these capabilities allow analysts to look broader, back, closer, and deeper to gather actionable insights.
Coastal Monitoring Systems
Satellite data can be leveraged in tools like early warning systems to detect and understand change across coastal areas. When powered by high-frequency and high-resolution Planet data, these systems allow governments to:
- Monitor the integrity of habitats and track water level variations
- Detect the early onset of algal blooms and red tides
- Assess potential degradation and understand erosion processes
- Observe sand accumulations and storm effects
- Anticipate and mitigate loss of land
- Prioritize rehabilitation activities
- Enhanced predictive models for flooding and other severe weather events
Ultimately, coastal monitoring solutions help agencies identify and understand change sooner, to make informed decisions that protect ecosystems and related communities.
Case Study: Mississippi Department of Marine Resources
In the United States, the Mississippi Department of Marine Resources (MDMR) is tasked with the mission to enhance, protect, and conserve the state’s marine interests. With territory along the U.S. Gulf Coast, MDMR manages diverse marine life and wetlands to ensure equitable use for environmental, recreational, and economic interests.
MDMR currently uses Planet data to confirm permitting compliance for development in protected areas under MDMR’s Coastal Zone Enhancement Program.
And in the future, MDMR plans to use Planet data to evaluate tidal marsh health and quality over time — from monitoring biodiversity and identifying sedimentation issues to tracking highly transient sea grasses in bayous threatened by storms.
The Future of Coastal Habitat Monitoring With Planet’s solutions
Governments and environmental organizations recognize the urgency to preserve coastal habitats. However, addressing these challenges requires comprehensive monitoring and data-driven decision-making.
Sustainable coastal management that leverages broad area management allows agencies to monitor coastal change at scale. With comprehensive, high-frequency Planet data, any area on Earth can be monitored and analyzed, no matter how large, small, or remote.
You can learn more about coastal monitoring strategies with broad area management in our e-book, Multidimensional Coastal Monitoring.
Or contact us — we’d love to discuss how Planet can help you meet environmental or policy goals.

Ready to Get Started
Connect with a member of our Sales team. We'll help you find the right products and pricing for your needs