Syngenta: Pioneering the Fight Against Harmful Nematodes with Satellite Data
You can also read this blog in Portuguese and Spanish.
In the world of agriculture, innovation is the key to overcoming challenges and ensuring food security for the growing global population. Syngenta, a pioneer in agricultural innovation, is once again at the forefront of change. With the help of Planet satellite data, Syngenta launched a tool that promises to revolutionize the battle against a hidden menace — harmful nematodes.
Plant-parasitic nematodes are microscopic parasites that lurk in the soil, feasting on the roots of crops. These tiny pests might be small, but they wreak havoc on plant health, crop quality, and yield. Globally, plant-parasitic nematodes are responsible for up to USD 150 billion in annual crop losses. Farmers around the world have been grappling with this invisible threat for decades.
Syngenta's pursuit of innovative solutions has led to the development of the world's first commercial digital tool for diagnosing damages and stress caused by plant-parasitic nematodes in soybean crops — aptly named Nema Digital. This tool leverages high-resolution satellite images, provided by Planet, and a proprietary algorithm to identify areas with high nematode infestations.
Nema Digital customers will have access to Planet imagery. This partnership leverages the capabilities of space technology to empower farmers with valuable insights. By offering actionable information, this tool allows growers to make informed choices, optimizing crop management and enabling them to select the most suitable products for their specific needs.
A Closer Look: Fighting Nematodes in Brazil
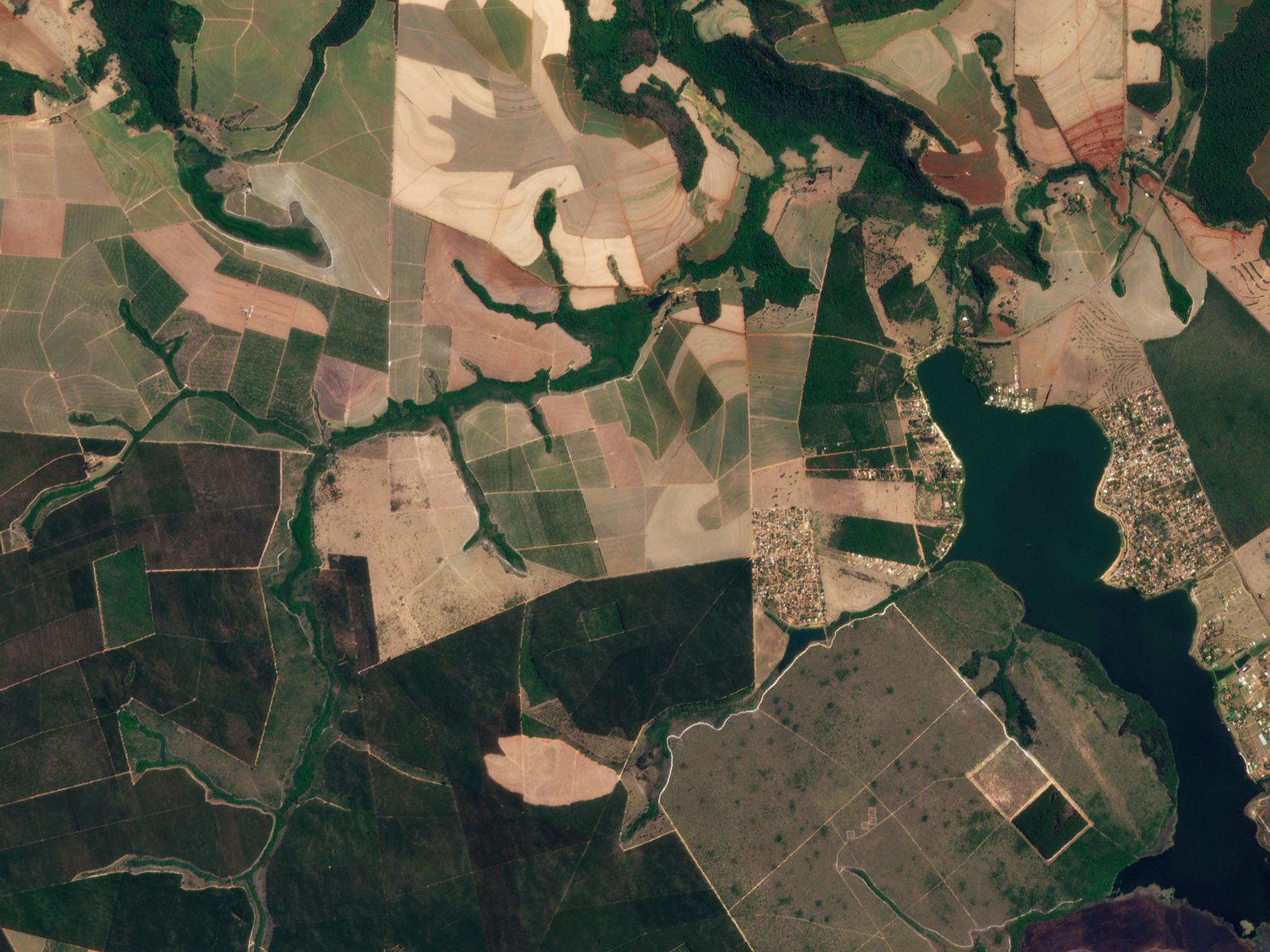
Last year, Syngenta deployed its digital nematode diagnosis and mapping tool as part of a pilot program in Brazil, specifically targeting 130,000 hectares of soybean farms. The chosen areas were afflicted with nematode infestations, a problem that plagues 90 percent of soybean land in the country. With approximately 35 percent of global soybean production happening in Brazil, the impact of plant-parasitic nematodes cannot be underestimated. These pests are estimated to cause over USD 5.4 billion in annual losses to soybean production in the country, with some regions experiencing yield losses of up to 30 percent due to nematode infestations.
This approach utilizes satellite imagery from both Sentinel 2 and Planet, enabling the generation of detailed maps highlighting nematode damage. By identifying anomalies in the soy canopy, farmers gain crucial insights at the beginning of the growing season.
Syngenta offers a corresponding service, guiding the collection of samples from potential nematode hotspots based on these initial maps. As the season progresses, another map is generated using in-season satellite imagery from Planet, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of nematode impact from start to finish. The tool's effectiveness has prompted its integration into Syngenta’s Cropwise platform as part of the Protector functionality. Cropwise is the global platform for crop optimization and digital agriculture from Syngenta, which currently has more than 40,000 users and monitors over 230 million acres.
The tool has officially been introduced to growers in Brazil, allowing them to access Nemagitial through Cropwise Protector as they begin their soybean cultivation this fall. It provides a streamlined system for report storage and offers a user-friendly dashboard and tools that allow for soil sampling, prioritization of fields for treatment, and identifying nematode-affected spots significantly enhancing modern farming practices.
Combining Sentinel and Planet imagery, this tool is an evolution of the former Gamaya method, ensuring the ability to consistently monitor fields during the critical points of the growing season, signifying a pivotal advancement in combating nematodes.

Ready to Get Started
Connect with a member of our Sales team. We'll help you find the right products and pricing for your needs